2022 FHA loan guide: Requirements, rates, and benefits
Why use an FHA loan?
FHA loans have been making homeownership more accessible for decades.
Tailored to borrowers with lower credit, FHA makes it possible to buy a house with a credit score of just 580 and only 3.5% down.
But home buyers aren’t the only ones who can benefit. For current homeowners, an FHA refinance may let you access low rates and home equity, even without great credit.
Not sure whether you’ll qualify for a mortgage? Check out the FHA program. You might be surprised.
Verify your FHA loan eligibility. Start here (Feb 5th, 2022)
In this article (Skip to…)
>Related: How to buy a house with $0 down: First–time home buyer
What is an FHA loan?
An FHA loan is a mortgage insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA).
FHA insurance protects mortgage lenders, allowing them to offer loans with low interest rates, easier credit requirements, and low down payments (starting at just 3.5%).
Thanks to their flexibility and low rates, FHA loans are especially popular with first–time home buyers, home shoppers with low or moderate incomes, and/or lower–credit home buyers.
But FHA financing isn’t limited to a certain type of buyer – anyone can apply.
Verify your FHA loan eligibility. Start here (Feb 5th, 2022)
FHA loan requirements
To qualify for an FHA home loan, you’ll need to meet these requirements:
- A 3.5% down payment if your credit score is 580 or higher
- A 10% down payment if your credit score is between 500–579
- A debt–to–income ratio (DTI) of 50% or less
- Documented, steady income and employment history
- You’ll live in the home as your primary residence
- You have not had a foreclosure in the last three years
These FHA loan requirements are a lot more lenient than other types of mortgages.
For instance, FHA allows borrowers with credit scores as low as 500, while the minimum credit score for most other loan types is 620 or higher.
And FHA allows debt–to–income ratios up to 50% in some cases, while conventional loans max out at 43%. That means if you have a lot of current debt, you’ll be more likely to qualify for a home mortgage with FHA.
Overall, these guidelines make it possible to buy a house through the Federal Housing Administration even if you don’t have a super high credit score or a ton of money saved up.
FHA loan rates
FHA loans usually have below–market interest rates. That means they’re lower, on average, than comparable conventional loans.
Today’s 30–year FHA loan rates start at % (% APR) for a borrower with strong credit*. By comparison, conventional mortgage rates begin at % (% APR) for a similar loan.
| Loan Type | Current Interest Rate* |
| 30-Year FHA Loan | % (% APR) |
| 30-Year Conventional Loan | % (% APR) |
| 15-Year FHA Loan | % (% APR) |
| 15-Year Conventional Loan | % (% APR) |
*Mortgage rate estimates come from TheMortgageReports lender network and are current as of today, February 5, 2022. You can see our full loan assumptions here.
Note, the APR on an FHA loan is often higher than the APR on a conventional loan. That’s because FHA rate estimates include mortgage insurance premiums, while conventional rate estimates assume 20% down and no private mortgage insurance.
“Keep in mind that the upfront mortgage insurance and annual mortgage insurance required by an FHA loan could cost more than a conventional loan with a slightly higher rate,” says Jon Meyer, The Mortgage Reports loan expert and licensed MLO.
For a borrower putting down 3% on a conventional loan (comparable to the 3.5% minimum down payment on an FHA loan), the APR would look a lot closer to the APR for an FHA mortgage.
Check your FHA rate today. Start here (Feb 5th, 2022)
How FHA loans work
The first thing to know about FHA mortgages is that the Federal Housing Administration doesn’t actually lend you the money.
You get an FHA mortgage loan from an FHA–approved bank or lender, just like you would any other type of home mortgage loan.
The FHA’s role is to insure these mortgages, offering lenders protection in case borrowers can’t pay their loans back. In turn, this lets mortgage lenders offer FHA loans with lower interest rates and looser standards for qualifying.
The one catch – if you want to call it that – is that you pay for the FHA insurance that protects your mortgage lender. This is called “mortgage insurance premium” or MIP. Here’s how it works.
FHA mortgage insurance
FHA mortgage insurance premium (MIP) is what makes the FHA program possible. Without the MIP, FHA–approved lenders would have little reason to make FHA–insured loans.
There are two kinds of MIP required for an FHA loan. One is paid as a lump sum when you close the loan, and the other is an annual premium, which becomes less expensive each year as you pay off the loan balance:
- Upfront Mortgage Insurance Premium (UFMIP) = 1.75% of the loan amount for current FHA loans and refinances
- Annual Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP) = 0.85% of the loan amount for most FHA loans and refinances
The good news is that, as a homeowner or home buyer, your FHA loan’s MIP rates have dropped. Today’s FHA MIP costs are now as much as 50 basis points (0.50%) lower per year than they were in 2014.
Also, you have ways to reduce what you’ll owe in FHA MIP.
Depending on your down payment and loan term, you can reduce the length of your mortgage insurance to 11 years instead of the entire loan.
| Loan term | Original down payment | MIP duration |
| 20, 25, 30 years | Less than 10% | Life of loan |
| 20, 25, 30 years | More than 10% | 11 years |
| 15 years or less | Less than 10% | Life of loan |
| 15 years or less | More than 10% | 11 years |
Or, you could refinance out of FHA MIP at a later date.
With rates as low as they are today, refinancing could reduce your monthly mortgage payments and cancel your mortgage insurance premium if you have enough equity in the home.
Check your FHA loan rates. Start here (Feb 5th, 2022)
FHA home loan benefits
There’s a lot to love about the FHA home loan program. Here are some of the biggest benefits:
- Low down payments
- Gifted funds permitted
- Higher DTIs allowed
- Lower credit scores allowed
- No credit scores eligible
- Sizable loan amounts
- Loan limits can be extended
- Refinancing available
1. Lower down payment: Just 3.5 %
For today’s home buyers, there are only a few mortgage options that allow for down payments of 5% or less. The FHA loan is one of them.
With an FHA mortgage, you can make a down payment as small as 3.5% of the home’s purchase price. This helps home buyers who don’t have a lot of money saved up for a down payment along with home buyers who would rather save money for moving costs, emergency funds, or other needs.
2. FHA allows 100% gift funds for the down payment and closing costs
The FHA is generous with respect to using gifts for a down payment. Very few loan programs will allow your entire down payment for a home to come from a gift. The FHA will.
Via the FHA, your entire 3.5% down payment can be a gift from parents or another family member, an employer, an approved charitable group, or a government homebuyer program.
If you’re using a down payment gift, though, you’ll need to follow the process for gifting and receiving funds.
3. FHA loans allow higher debt–to–income ratios
FHA loans also allow higher debt–to–income ratios.
Your debt–to–income ratio, or DTI, is calculated by comparing two things: your debt payments and your before–tax income.
For instance, if you earn $5,000 a month and your debt payment total is $2,000, your DTI is 40%.
Officially, FHA maximum DTIs are as follows.
- 31% of gross income for housing costs
- 43% of gross income for housing costs plus other monthly obligations like credit cards, student loans, auto loans, etc.
However, a 43% DTI is actually on the low end for most FHA borrowers.
Mortgage software company ICE Mortgage Technology recently reported that throughout 2021, the average DTI for closed FHA purchases was about 44%.
And FHA will allow DTI ratios as high as 50%. Although to get approved at such a high ratio, you’ll likely need one or more compensating factors – for instance, a great credit score, significant cash savings, or a down payment exceeding the minimum.
In any case, FHA is more lenient in this area than other loan programs.
Most conventional mortgage programs – those offered by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac – only allow debt–to–income ratios between 36% and 43%.
With down payments of less than 25%, for example, Fannie Mae lets you go to 43% DTI for FICOs of 700 or higher. But most people don’t get conventional loans with debt ratios that high.
ICE Mortgage Technology reported that in 2021, the average DTI for closed conventional purchases was 35% compared to 44% for FHA loans.
4. FHA loans accept lower credit scores
Officially, the minimum credit scores required for FHA mortgage loans are:
- 580 or higher with a 3.5% down payment
- 500–579 with a 10% down payment
Though in fact, the average credit score for FHA buyers was 678 in 2021.
High credit scores are great if you have them. But past credit history mistakes take a while to repair.
FHA loans can help you get into a home without waiting a year or more for your good credit to reach the “excellent” level.
Other loan programs are not so forgiving when it comes to your credit rating.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (the agencies that set rules for conventional loans) say they accept FICOs as low as 620. But in reality, some lenders impose higher minimum credit scores.
Stricter credit score minimums are part of the reason the average credit score for completed Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac home purchase loans was 757 in 2021 – nearly 80 points higher than the average FHA score.
5. FHA even permits applicants with no credit scores
What if an applicant has never had a credit account? Their credit report is, essentially, blank.
FHA borrowers with no credit scores may also qualify for a mortgage. In fact, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) prohibits FHA lenders from denying an application based solely on a borrower’s lack of credit history.
The FHA allows borrowers to build non–traditional credit as an alternative to a standard credit history. This can be a huge advantage to someone who’s never had credit scores due to a lack of borrowing or credit card usage in the past.
Borrowers can use payment histories on items such as utility bills, cell phone bills, car insurance bills, and apartment rent to build non–traditional credit.
“Not all lenders who are FHA approved offer these types of loans, so check with each lender individually,” cautions Meyer.
6. FHA loans can be up to $ in most of the U.S.
Most mortgage programs limit their loan sizes, and many of these limits are tied to local housing prices.
FHA mortgage limits are set by county or MSA (Metropolitan Statistical Area), and range from $ to $ for single–family homes in most parts of the country.
Limits are higher in Alaska, Hawaii, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Guam, and also for duplexes, triplexes, and four–plexes.
7. FHA also allows extended loan sizes
As another FHA benefit, FHA loan limits can be extended where home prices are more expensive. This lets buyers finance their home using FHA even though home prices have skyrocketed in certain high–cost areas.
In Orange County, California, for example, or New York City, the FHA will insure up to $ for a mortgage on a single–family home.
For 2–unit, 3–unit and 4–unit homes, FHA loan limits are even higher – ranging up to $.
If your area’s FHA’s loan limits are too low for the property you’re buying, you’ll likely need a conventional or jumbo loan.
8. If you have an FHA loan, you can lower your rate with an FHA Streamline Refinance
Another advantage for FHA–backed homeowners is access to the FHA Streamline Refinance.
The FHA Streamline Refinance is an exclusive FHA program that offers homeowners one of the simplest, quickest, and most affordable paths to refinancing.
An FHA Streamline Refinance requires no credit score checks, no income verifications, and home appraisals are waived completely.
In addition, via the FHA Streamline Refinance, homeowners with a mortgage pre–dating June 2009 get access to reduced FHA mortgage insurance rates.
Verify your FHA loan eligibility. Start here (Feb 5th, 2022)
FHA loan pros and cons
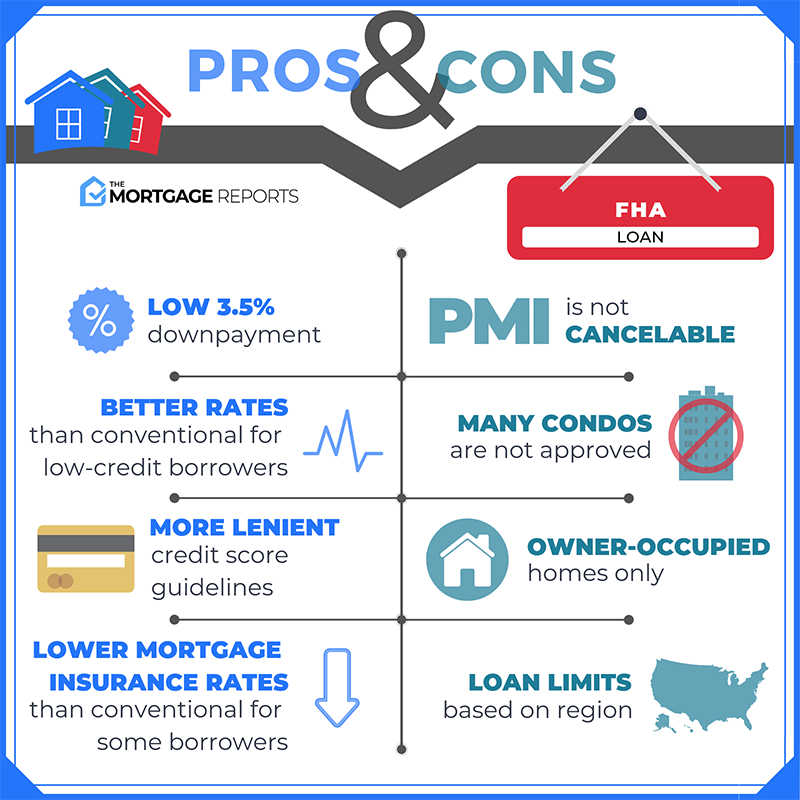
FHA Loan FAQ
Anyone can apply for an FHA loan; you do not need to be a first–time home buyer. However, FHA borrowers do need a credit score of 580 or higher; a debt–to–income ratio of 45 percent or less; a down payment of at least 3.5 percent; a steady, documented employment history and income; and you must plan to live in the home as your primary residence. Finally, the home needs to pass an FHA appraisal and the mortgage must be within current FHA loan limits. Unlike USDA mortgage loans, FHA does not set income requirements.
FHA loans are often considered easier to get than other types of mortgages. One reason is that they have lower credit score requirements. FHA loans allow FICO scores starting at 580 in most cases, while conventional loans start at 620. FHA also allows a higher debt–to–income ratio, which is good news for borrowers with big debts, like student loans and auto loans. Finally, FHA loans only require 3.5 percent down, and the whole down payment can come from gift funds or down payment assistance if the buyer finds financial aid.
There is no income limit to qualify for an FHA loan. You can apply with any salary. However, you must meet the minimum FICO score and remain under the maximum debt–to–income limit.
The biggest downside to an FHA loan is its expensive mortgage insurance. Unlike conventional loans, FHA mortgage insurance cannot be canceled once you build up equity. However, it is possible to refinance out of an FHA loan and into a conventional loan without private mortgage insurance once you reach 20 percent equity. If you have lower credit or other roadblocks to mortgage qualifying, an FHA can help you get into a home now with a plan to refinance and lower your overall costs later.
The loan amount you’ll qualify for with an FHA loan depends on a number of factors, including your credit score, interest rate, debt–to–income ratio, down payment, and more. However, you cannot qualify for more than the FHA loan limit. This varies based on location and the number of units in the home you’re buying. You can get pre–approved with a lender to see how large of an FHA loan you qualify for.
Most lenders are FHA–approved. This includes mortgage lenders, big banks, and credit unions. The marketplace for FHA loans is giant, which creates competitive pressure among lenders to offer low FHA rates and low FHA fees. So it pays to shop around on an FHA loan. Also, because different banks use different methods to underwrite, your FHA loan can be declined by Bank A but approved by Bank B. If you meet the rules of the FHA, you can apply until your loan gets approved.
FHA offers standard, 30–year fixed–rate mortgages and 15–year fixed–rate mortgages. Borrowers can also use an FHA 5/1 adjustable–rate mortgage (ARM) if they wish. In addition, FHA insures purchase–and–improvement loans for when you want to buy a home that needs repairs; construction loans for when you want to buy a home that’s newly built; and energy–efficiency loans for when you want to finance the costs of energy–efficiency improvements into your loan. The FHA also provides a full line of FHA refinance products, including the low–doc FHA Streamline Refinance.
The FHA will insure single–family detached homes, 2–unit homes, 3–unit homes, 4–unit homes, condominiums, mobile homes, and manufactured homes. If you’re buying a multi–unit home, you’ll need to use one of the units as your primary residence. In addition, FHA home buyers can purchase any home type in any U.S. neighborhood – whether in the 50 United States, the District of Columbia, or any U.S. territory.
FHA loans require both an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UMIP) when the loan closes and an annual fee (MIP) that is split up and distributed across your monthly mortgage payments. The upfront fee is 1.74 percent of the loan amount. MIP is based on home value but is often around 0.85 percent of the loan amount.
You can get rid of your FHA mortgage insurance premiums by refinancing into a non–FHA loan. The most popular type of loan to refinance into is a conventional mortgage.
Yes. A little–known FHA benefit is that the agency will allow a home buyer to assume the existing FHA mortgage on a home being purchased. The buyer must still qualify for the mortgage with its existing terms but, in a rising mortgage rate environment, it can be attractive to assume a home seller’s loan. Five years from now, for example, a buyer of an FHA–insured home could inherit a seller’s sub–3 percent mortgage rate. This can make it easier to sell the home in the future.
Via its 203k program, the FHA offers construction loans to home buyers planning upgrades to a new home; and homeowners planning to make repairs to a home already owned. Accepted 203k loan projects include new roofing, structural additions, and complete home tear–downs. The 203k loan can be applied to homes in need of minor repairs as well as fixer–uppers.
You can’t buy a true rental property with an FHA loan. However, you can buy a multi–unit property – a duplex, triplex, or fourplex – live in one of the units, and rent out the others. The rent from the other units can partially, or even fully, offset your mortgage payment.
Loan–to–value (LTV) is another way to talk about down payments. Your LTV ratio compares your home value to your loan amount – or, put differently, the amount you’re borrowing after your down payment. For instance, if you put 3.5 percent down using an FHA loan, your LTV is 96.5 percent because you’re borrowing 96.5 percent of the purchase price. LTV is also important when you refinance because it shows how much you still owe on your mortgage compared to your home’s current value.
FHA mortgage underwriting isn’t too much more complicated than underwriting for a conventional loan. Both loan types require you to document your employment history using pay stubs or tax returns. And both require a thorough check of your credit history and score. However, the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development does set minimum property standards for FHA properties. These standards ensure homes are safe, secure, and physically sound. To purchase your home using an FHA loan, the property will have to pass an FHA appraisal to make sure it meets these standards.
Closing costs are about the same for FHA and conventional loans with a couple of exceptions. First, the appraiser’s fee for an FHA loan tends to be about $50 higher. Also, if you choose to pay your upfront MIP in cash (instead of including this 1.75% fee in your loan amount), this one–time fee will be added to your closing costs. Additionally, the fee can be rolled into your loan amount.
Not really. In the early days of the coronavirus pandemic, mortgage lenders tightened restrictions. Since FHA lenders can set their own borrowing requirements, this affected FHA home buyers along with conventional borrowers. But lenders soon loosened these restrictions, especially as mortgage rates continued to drop. Home buyers can still get easy access to FHA–backed mortgage loans. With stay–at–home orders in place in many states, more borrowers have applied for FHA loans online this year.
Most borrowers will need a minimum credit score of 580 to get an FHA loan. However, home buyers who can put at least 10% down are eligible to qualify with a 500 score. Yet, each lender may have their own credit score minimums, separate to those established by the Federal Housing Administration.
Alternatives to FHA home loans
There are several government–backed and non–government (conventional) options that also offer low down payments and flexible underwriting. They include:
FHA mortgage eligibility is not restricted to first–time or low–income buyers. Alternatives like VA mortgages are limited to eligible military and veteran applicants, and USDA loans have income restrictions and are available in less densely populated areas.
Conforming and conventional loans often require higher credit scores.
No single mortgage program is best for all home buyers, so it’s smart to compare.
Today’s FHA loan rates
Current mortgage rates are hovering near record lows. And FHA rates are generally among the lowest.
Compare rates from FHA–approved lenders to find the most affordable loan. You can get started right here.
The information contained on The Mortgage Reports website is for informational purposes only and is not an advertisement for products offered by Full Beaker. The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the author and do not reflect the policy or position of Full Beaker, its officers, parent, or affiliates.
Comments are closed.